MLZ is a cooperation between:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ is a member of:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ on social media:

MLZ (eng)
Lichtenbergstr.1
85748 Garching
KOMPASS (in commissioning)
Cold three axes spectrometer with polarisation analysis
This instrument is focussed on cold neutrons. All parameters given here are valid during the current operation of FRM II. Please get in touch with the instrument team well in advance for all further details (length of experiment etc.).
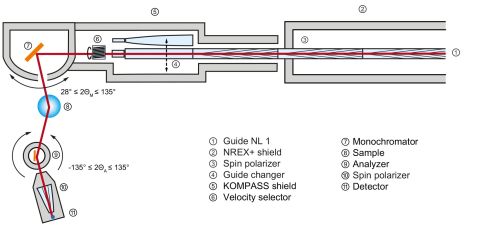
KOMPASS — the new cold neutron three axes spectrometer is fully designed to work exclusively with polarized neutrons and to provide a zero-field 3D polarization analysis, complementary to the other three axes spectrometers at the FRM II. Typical applications are the investigations of complex and weak magnetic structures and dynamics.
The instrument is located at the end position of the curved, cold neutron guide NL 1 in the Neutron Guide Hall West. Serial cavities in the first part of the guide system provide a permanent high-polarized incident neutron beam. The parabolic focusing guide design before the monochromator further includes different guide front ends for an optimized energy- and Q-resolution, respectively. The focusing guide together with the variable double-focusing monochromator (and analyzer) provide a high neutron flux over a large dynamic range at a small sample volume and a superior energy resolution at the expense of a slightly reduced transverse Q-resolution. For measurements with high Q-resolution, or for the investigation of steep dispersion relations, the parabolic front ends can be exchanged for straight elements. Higher-order wavelength contaminations can be suppressed by an optional velocity selector in front of the monochromator. For sample positioning the sample table is equipped with motorized xy-stages and cradles. The spin state of the scattered neutrons is analyzed with a multi-channel polarizer situated between the analyzer and the detector.
Apart from a standard closed-cycle cryostat, the instrument will be equipped with a set of Helmholtz coils for longitudinal polarization analysis and the 3rd generation ILL system CryoPAD for the neutron polarimetry.
Construction and commissioning of KOMPASS are supported by the BMBF through project 05K19PK1.
- all types of weak magnetic orders
- complex (chiral) magnetic structures (e.g. rare-earths)
- quantum effects associated with longitudinal magnetic excitations
- quantum critical fluctuations
- systems of reduced dimensions (e.g. thin films and multilayer structures)
- multiferroic and magneto-electric materials
- high-TC-superconductors
- itinerant magnetic systems
Please note: With thermal neutrons, KOMPASS will be mainly operated in polarized neutron diffraction mode with longitudinal polarization analysis.
- End position of the neutron guide NL1, dimensions: 60 × 120 mm2 (W × H)
- Permanently installed triple polarizing V-cavity providing high incident polarization of P > 98 %
- Parabolic focusing in the scattering plane
- Exchangeable straight and parabolic focusing guide front ends for optimized (E,Q)-resolution
- Compact design with M-S and S-A distances of only 120 cm, A-D distance of 100 cm.
- Δλ/λ = 31 %, effective down to λmin = 2.35 Å wavelength
- Effectively suppresses higher order contaminations and lowers the background
- Selector can be exchanged with “virtual source” slit-system located in the focus point of the parabolic polarizing guide
- HOPG (d = 3.355 Å), dimensions: 273 × 188 mm2 (W × H)
- 28° < 2ΘM < 135°
- 1.04 Å-1 < ki < 3.87 Å-1
- Doubly variable focusing
- HOPG (d = 3.355 Å), dimensions: 220 × 225 mm2 (W × H)
- -130° < 2ΘA < 130°
- Doubly variable focusing
- Optional Heusler Analyser with variable horizontal focusing (from PANDA)
- Compact polarizing V-cavity
- 5 channels with double-sided Fe/Si coated silicon wafers, m = 4.2
- Pf >96 % for neutrons with 1.5 ≤ En ≤ 15 meV
- Optional 10’ and 30’ horizontal collimators
- Integrated Hallbach Array
- 2” ³He tube (standard)
- 1” PSD ³He tube with active length of 250 mm (optional)
- α0: 20’, 40’
- α1: 10’, 20’, 40’, 80’
- α2: 10’, 20’, 40’, 80’
- α3: 10’, 20’, 40’, 80’
- 30’and 60’ radial collimators between focused analyser and detector for suppression of HOPG diffuse scattering
- Incident energy range: 2.2 meV < Ei < 25 meV
- Scattering angle at the sample: 2ΘS up to 140°
- Analyser scattering angle: -130°< 2ΘA < 130°
- Energy transfer: up to 20 meV
- Momentum transfers : up to Q = 5 Å-1
Instrument Scientists
Prof. Dr. Markus Braden (project leader)
Phone: +49 (0)221 470-3655
E-Mail: Braden@ph2.uni-koeln.de
Prof. Dr. Peter Böni (project leader)
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-14711
E-Mail: Peter.Boeni@frm2.tum.de
Dr. Dmitry Gorkov (instrument scientist)
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-10754
E-Mail: Dmitry.Gorkov@frm2.tum.de
KOMPASS
Phone: +49 (0)89 289-14879
Operated by

Funding

Publications
Find the latest publications regarding KOMPASS in our publication database iMPULSE:
Instrument control


MLZ is a cooperation between:
 > Technische Universität München
> Technische Universität München > Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
> Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon
 > Forschungszentrum Jülich
> Forschungszentrum Jülich
MLZ is a member of:
 > LENS
> LENS > ERF-AISBL
> ERF-AISBL
MLZ on social media: